Knee Treatments
Treating knee injuries can range from conservative care to surgical procedures, depending on the severity of the injury. While minor injuries might respond well to physical therapy and resting at home, more serious injuries like ligament tears often require surgical intervention.
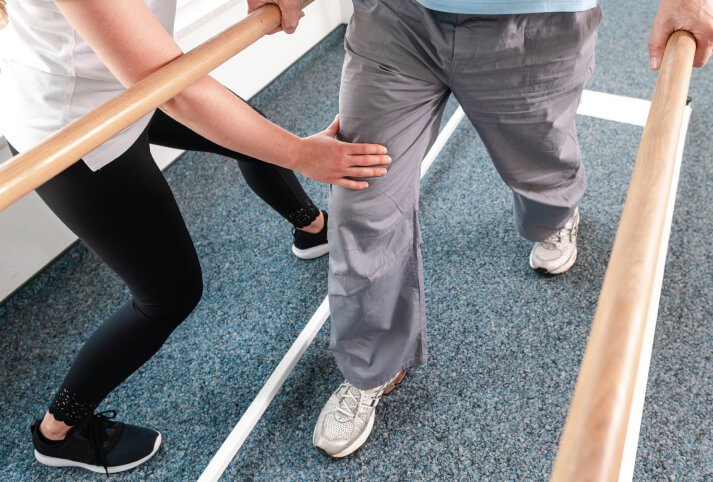

Non-Surgical Knee Treatments
For less critical cases, conservative measures help to reduce the pain and improve function. Some common treatments include:
- Rest and rehabilitation – Most mild knee injuries respond well to the RICE method (rest, ice, compression, elevation) together with physical therapy to restore strength and mobility in the joint.
- Medications – Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications help to reduce pain and swelling, as well as manage inflammation.
- Bracing and support – Knee braces or supports help stabilise the joint and limit movement to prevent further injury.
- Injections - Injected directly into the knee joint, these are aimed at reducing pain and inflammation especially in arthritic joints. They include steroid, hyaluronic acid, or platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections.
- Lifestyle modifications - This includes losing excess weight, avoiding high-impact activities (e.g. running) and switching to low-impact workouts (e.g. swimming) to lessen the stress on the knee joint until it recovers.
Surgical Knee Treatments
Knee surgery addresses a variety of severe injuries and conditions affecting the knee joint. Whether due to sudden trauma, degenerative disease, or chronic wear and tear, knee issues can negatively affect a person’s mobility and daily life. The goal of knee surgery is to relieve pain, restore function and improve overall joint movement. Some common types of knee surgeries are:
There are two types of meniscus surgery the surgeon may perform on the torn meniscus (depending on its severity):
- Meniscus repair – Stitching the tear back together
- Meniscectomy – The entire or part of the damaged meniscus is removed
Let our knee specialist guide you through the options for a smooth recovery.

Preparing For A Knee Surgery
- Preoperative assessment – Physical exam, X-rays, MRI scans will be conducted to determine the best surgical approach. The patient will also meet with the surgeon and anaesthesiologist.
- Lifestyle adjustments – To improve the outcome of the surgery, the patient might be recommended to adapt some lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking and eating healthy.
- Planning for recovery – Post surgery, patients might need mobility aids like crutches or a walker when recovering at home. It might also be good to have someone to assist during the first few days.
Knee Surgery Risks
As with surgical procedure, there are some risks and complications that accompany knee surgery, even though they are rare.
Some potential risks that could come with undergoing knee surgery include:
- Infection
- Blood clots
- Implant failure (during knee replacement surgery)
- Persistent pain or stiffness
- Nerve or blood vessel damage
Your surgeon will discuss these risks with you before the procedure.

Camden Medical
1 Orchard Boulevard, #09-06, Singapore 248649
Mount Alvernia Hospital
820 Thomson Road, Medical Centre D #05-60, Singapore 574623
Contact Information
Tel : 8028 4572
Mobile : 8028 4572
Whatsapp : 8028 4572
Email : hello@quantumortho.com.sg
Operating Hours
Monday-Friday : 8:30am - 5:30pm
Saturday : 8:30am - 12:30pm
Sunday & Public Holiday : Closed
