Knee Conditions
Experiencing Knee Pain & Injury?
Knee pain can arise from injuries due to accidents and falls, general wear and tear, or diseases like arthritis and gout. Left untreated, knee pain can worsen over time, affecting mobility and daily activities. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing further damage and ensuring long-term joint health.
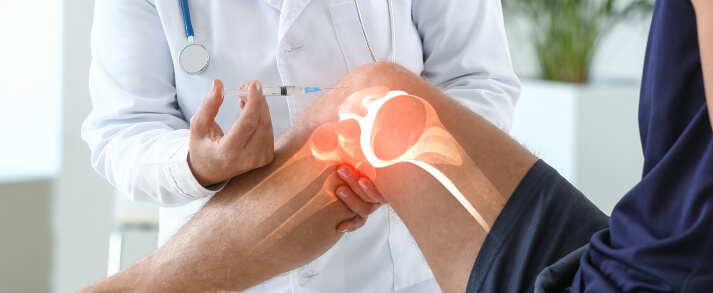
Common Knee Injuries We Treat
Knee injuries involve damage to the bones, ligaments, cartilage, tendons, or muscles surrounding the knee. They can vary from minor strains to complete tears, significantly impacting a person’s mobility and quality of life.
Ligament Injuries
Ligament injuries occur when the bands of connective tissue that stabilise the knee joint are stretched, or partially or completely torn. These are common among athletes who frequently perform movements that involve sudden impacts, stops or rotations to the knee.
- ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) tears
- PCL (posterior cruciate ligament) tears
- MCL (medial collateral ligament) tears
- LCL (lateral cruciate ligament) tears
- Ligament sprains
Meniscus Tears
Meniscus tears occur when the cartilage cushioning the knee joint (menisci) is torn, due to twisting the knee while bearing weight, or due to degeneration when the meniscus starts to wear down with age.
These tears can also happen due to degeneration over time, as the meniscus gradually wears down with age, leading to increased vulnerability and a higher risk of injury.
Tendon Injuries
Tendons are flexible tissues that connect muscles to bones; these can become inflamed or damaged. These include:
- Patellar Tendonitis – Caused by repetitive stress on the patellar tendon (which connects the kneecap to the shinbone) arising from jumping or running.
- Patellar Tendon Rupture – A more severe injury that happens when the tendon is overstretched or there is direct impact to the front of the knee, leading to a complete tear.
Fractures & Dislocations
A type of knee fracture is a patellar (kneecap) fracture, where there is a crack or break in the kneecap after experiencing significant trauma like a car accident or a fall.
Knee dislocations happen when the bones of the knee joint are forced out of alignment. This can involve just the patellar or the entire knee joint.
Other Conditions
- Knee Bursitis: This refers to the inflammation of the bursae, which are small fluid-filled sacs that reduce friction in the knee joint. The inflammation may come from prolonged kneeling or direct trauma.
- Knee Osteoarthritis: A degenerative condition where the cartilage in the knee is worn down over time, resulting in stiffness and chronic pain.
- Runner’s Knee (Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome): Occurs when the kneecap is slightly out of alignment and moves too much to one side, due to muscle imbalance or repetitive stress. This can lead to pain around or behind the kneecap.
- Knee Pain: Knee pain can result from injuries, overuse, or age-related wear and tear, affecting one’s mobility and quality of life. The sensation can range from a dull ache to sharp pain, and may be accompanied by tenderness or warmth around the joint. kneecap.
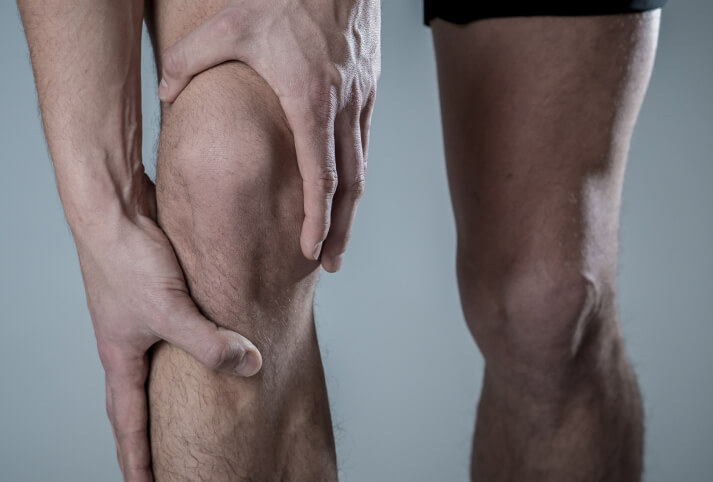
Signs & Symptoms of Knee Injuries
Knee injury symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity of the injury. Some symptoms may be mild, while others may require prompt medical attention. Being able to identify these symptoms early on can result in timely treatment.
Signs and symptoms arising from a knee injury usually include:
- Pain ranging from a dull ache to a sharp discomfort
- Swelling and bruising around the knee
- Stiffness or limited ability to bend or straighten the knee
- Instability or the knee "giving way” when walking or standing
- Popping or clicking at the time of the injury
- Locking or sudden inability to move the knee at all
- Inability to bear weight on the affected leg
Early intervention can make all the difference.
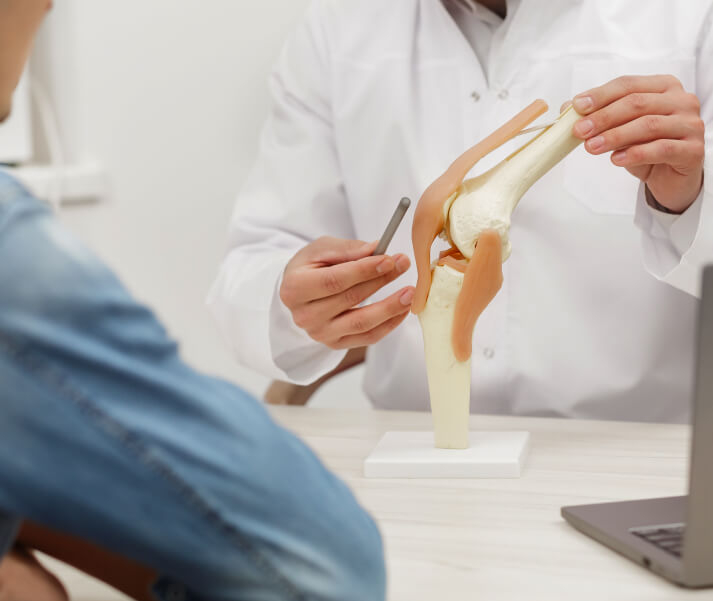
How is a Knee Injury Diagnosed?
Proper diagnosis of a knee injury involves a detailed physical evaluation, range-of-motion tests and imaging tests, so that the doctor can assess the knee’s internal structures clearly:
- X-Rays – These are used to detect bone fractures and bone joint degeneration; they are usually the first step when examining trauma or structural problems.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) – These use radio waves and strong magnets to detect tears in the ligaments, tendons, cartilages, and menisci, and show the extent of the damage.
- Ultrasound – This test is used to visualise tissue structures in real-time; it can detect injuries like patellar tendonitis and bursitis.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan – CT scans can provide a cross-sectional image of the bones and soft tissues to assess for complex bone fractures.
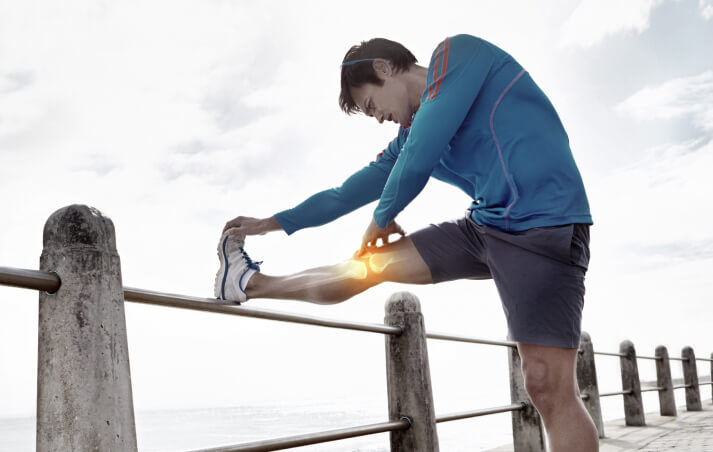

Preventing Knee Injuries
While not all knee injuries can be prevented, you can certainly lower your risk by adopting certain preventive measures:
- Strengthening exercises for muscles surrounding the knee
- Flexibility stretches to reduce tension in the knee joint and improves the range of motion
- Wearing proper footwear that provides sufficient cushioning and stability, especially during physical activities
- Maintain a healthy weight, as excess weight puts more pressure on the knee joints and might increase risk of reinjury

Camden Medical
1 Orchard Boulevard, #09-06, Singapore 248649
Mount Alvernia Hospital
820 Thomson Road, Medical Centre D #05-60, Singapore 574623
Contact Information
Tel : 8028 4572
Mobile : 8028 4572
Whatsapp : 8028 4572
Email : hello@quantumortho.com.sg
Operating Hours
Monday-Friday : 8:30am - 5:30pm
Saturday : 8:30am - 12:30pm
Sunday & Public Holiday : Closed
